Surety bonds and insurance are two types of financial protection. Surety bonds guarantee that a person or company will fulfill their obligations, while insurance pays for losses if something goes wrong.
In this guide, we’ll break down the core differences between surety bonds vs. insurance. That way, you’ll know how each will serve you best.
What’s the difference between a surety bond vs. insurance?
Insurance Overview
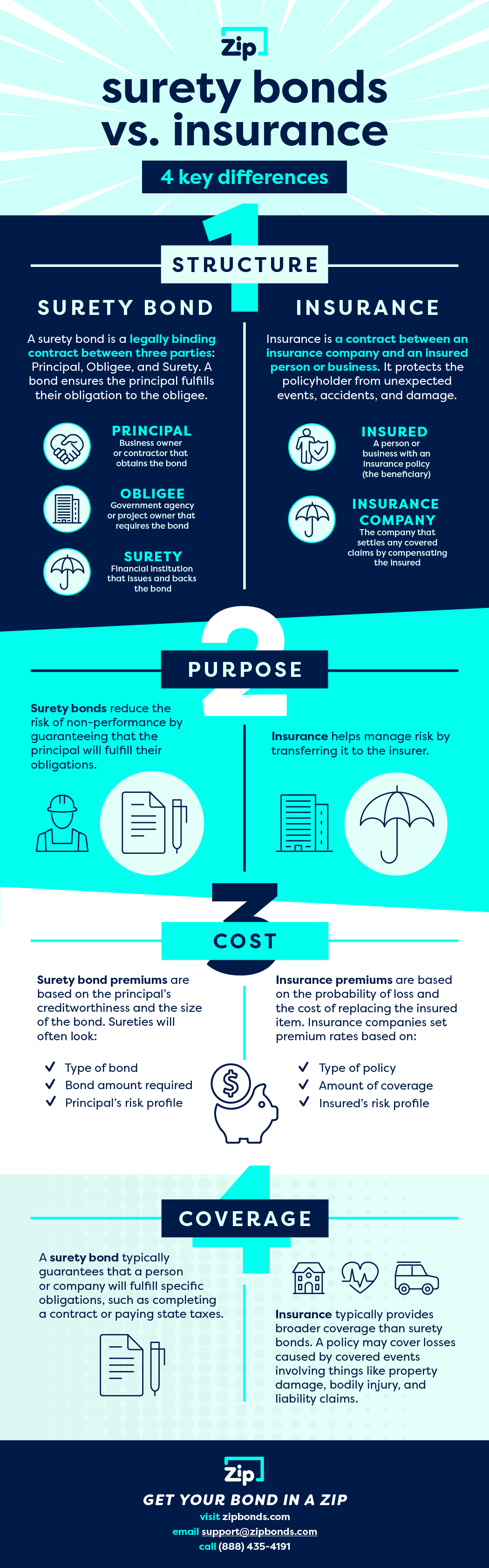
Insurance is a contract between an insurance company and an insured (an insured person or business). Insurance protects the policyholder from unexpected events, accidents, and damage. Common types of insurance include auto, homeowners, and health insurance. The insurance company agrees to pay for losses covered by the policy up to the policy limit.
TLDR: The insured person or business pays a premium to the insurance company in exchange for protection.
Surety Bond Overview
A surety bond is a three-party legal contract in which a surety (usually a bonding company) agrees to be responsible for the debt or obligation of a principal (the person or company seeking the bond) to an obligee (the person or company the principal owes a debt or obligation).
The surety bond guarantees the principal will fulfill their obligation to the obligee. If the principal fails and costs the obligee money, the surety company will step in and provide financial assistance and expertise to the obligee.
TLDR: A surety bond protects the obligee, not the principal.
Surety Bonds vs. Insurance: The Showdown
| Product | Responsible for Purchasing | Who It Protects | Responsible for Paying Out | Number of Parties Involved |
| Surety Bonds | Principal | Obligee | Surety and principal | 3 (principal, obligee, surety) |
| Insurance | Consumer | Policyholder | Insurance company | 2 (consumer and insurance company) |
1. Protection (Coverage)
Insurance typically provides broader coverage than surety bonds. For example, an insurance policy may cover losses caused by covered events involving things like property damage, bodily injury, and liability claims.
On the other hand, a surety bond is typically used to guarantee that a person or company will fulfill specific obligations, such as completing a contract or paying back a loan.
2. Guarantee
With insurance, the insurance company is the one who is ultimately responsible for paying for losses.
With a bond, the surety company is responsible for paying for losses upfront, but the principal is liable for repaying them for all covered costs. This means the principal must be prepared to reimburse the surety company for any losses paid out.
3. Premiums
Insurance premiums are based on the probability of loss and the cost of replacing the insured item. Insurance companies set premium rates based on the following factors:
- The type of policy
- Amount of coverage
- The insured party’s risk profile
Surety bond premiums are based on the principal’s creditworthiness and the size of the bond. Sureties will often look at these factors:
- Type of bond
- Amount of the bond
- The principal’s risk profile
Insureds typically pay a monthly or annual recurring premium. A surety bond can be a one-time or yearly cost.
4. Losses & Claims
With insurance, the insured party typically files a claim with the insurance company if they experience a loss covered by their policy. The insurance company will then investigate the claim and, if it’s valid, will pay the insured party for their losses.
With a surety bond, the obligee typically files a claim with the surety company if the principal fails to fulfill their obligations. The surety company will then investigate the claim and, if valid, will compensate the obligee for losses.
5. Who You Work With
You’ll typically work with an insurance agent or broker to get insurance. The agent or broker will help you choose the right policy for your needs and can help you file a claim if you experience a loss.
You’ll typically work with a surety bond provider to get a surety bond. Sometimes, they will review the applicant’s financial information and credit history before issuing your bond. Other times applicants can apply online and get approved for a bond immediately.
6. Parties Involved
With insurance, there are two main parties involved:
- An insured person or company (the beneficiary)
- The insurance company
The insured party pays premiums to the insurance company in exchange for protection against losses. Then if the insured experiences a covered loss, the insurance company will settle the claim by compensating the insured.
With a surety bond, there are also three parties involved:
- A principal
- A surety company
- An obligee (the beneficiary)
The principal pays a premium to the surety company in exchange for a guarantee that the principal will fulfill their obligations. If the principal fails to meet their obligations, the surety company will pay the obligee for their losses. They will then seek reimbursement from the principal.
7. Risk Management
Insurance helps manage risk by transferring it to the insurer. Surety bonds reduce the risk of non-performance by guaranteeing that the principal will fulfill their obligation.
Again, insurance mitigates risk for the insured. Surety bonds reduce the risk for the party that requires the bond (the obligee) even though the principal is the one that must purchase the bond.
Get Your Surety Bonds with ZipBonds
Contact the ZipBonds team to apply for your surety bond today! We offer thousands of bonds, including court, construction, fidelity, and license and permit bonds. You can always reach us by calling (888) 435-4191 or emailing support@zipbonds.com. We’ll help you get bonded in a zip!

